As you know that Hibernate works with normal Java objects that your application creates with the new operator. In raw form (without annotations), hibernate will not be able to identify your java classes, but when they are properly annotated with required annotations then hibernate will be able to identify them and then work with them e.g. store in DB, update them etc. These objects can be said to mapped with hibernate.
Given an instance of an object that is mapped to Hibernate, it can be in any one of four different states: transient, persistent, detached or removed.
Transient Object
Transient objects exist in heap memory. Hibernate does not manage transient objects or persist changes to transient objects.
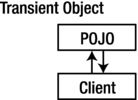
Transient objects are independent of Hibernate
To persist the changes to a transient object, you would have to ask the session to save the transient object to the database, at which point Hibernate assigns the object an identifier and marks the object as being in persistent state.
Persistent Object
Persistent objects exist in the database, and Hibernate manages the persistence for persistent objects.
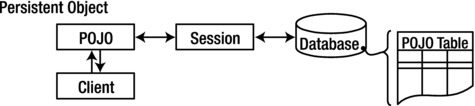
Persistent objects are maintained by Hibernate
If fields or properties change on a persistent object, Hibernate will keep the database representation up to date when the application marks the changes as to be committed.
Detached Object
Detached objects have a representation in the database, but changes to the object will not be reflected in the database, and vice-versa. This temporary separation of the object and the database is shown in image below.

Detached objects exist in the database but are not maintained by Hibernate
A detached object can be created by closing the session that it was associated with, or by evicting it from the session with a call to the session’s
evict() method.
In order to persist changes made to a detached object, the application must reattach it to a valid Hibernate session. A detached instance can be associated with a new Hibernate session when your application calls one of the load, refresh, merge, update(), or save() methods on the new session with a reference to the detached object. After the call, the detached object would be a persistent object managed by the new Hibernate session.
Removed Object
Removed objects are objects that are being managed by Hibernate (persistent objects, in other words) that have been passed to the session’s remove() method. When the application marks the changes held in the session as to be committed, the entries in the database that correspond to removed objects are deleted.
Key Points
- Newly created POJO object will be in the transient state. Transient object doesn’t represent any row of the database i.e. not associated with any session object. It’s plain simple java object.
- Persistent object represent one row of the database and always associated with some unique hibernate session. Changes to persistent objects are tracked by hibernate and are saved into database when commit call happen.
- Detached objects are those who were once persistent in past, and now they are no longer persistent. To persist changes done in detached objects, you must reattach them to hibernate session.
- Removed objects are persistent objects that have been passed to the session’s remove() method and soon will be deleted as soon as changes held in the session will be committed to database.


